layout: default- TOC {:toc}
USB Debugging on Android
If you have a personal device that you wish to use with Android Studio, enabling USB debugging is an important step in getting feedback sent from your phone to your PC. Setting this up, however, requires you to enable Developer Mode on your device.
-
Open the
Settingsapp on your device. -
Scroll down to the
About Phonesubmenu within theSettingsapp. This may be nested in a syntactically similar menu, such asSystem, and/or have a slightly different name. -
Scroll down to
Build Numberin theAbout Phonesubmenu. -
Tap
Build Numberseveral times. After a few taps, a Toast should appear notifying you that you are now a developer. -
Back out of the
About Phonesubmenu. You should now see aDeveloper Optionssubmenu on your device, somewhere in the same category asAbout Phone. -
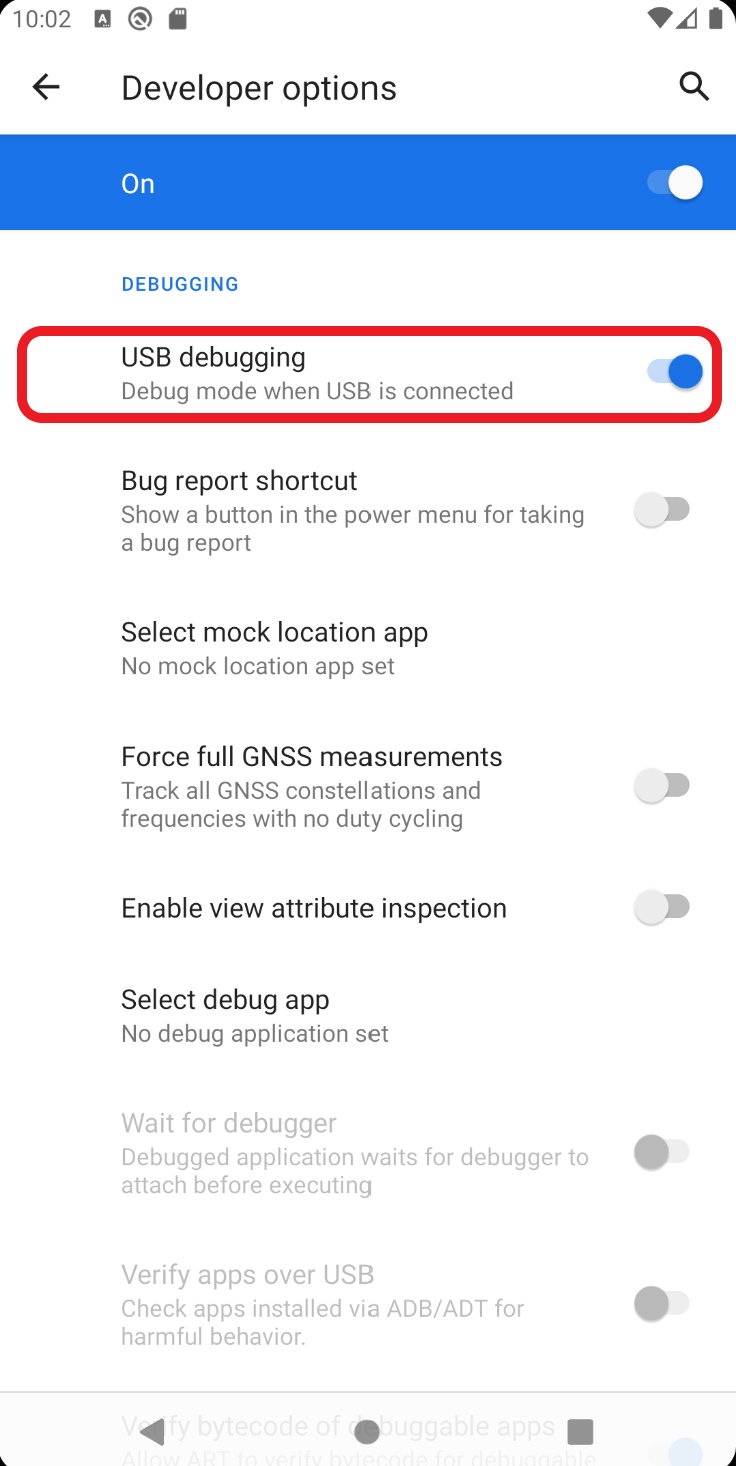
In the
Developer Optionssubmenu, you should have the option to enable USB debugging.
Once you have done that, you will be able to debug your applications directly from your device.
Debugging Strategies
-
As with JGRASP, you can set breakpoints in your code by clicking to the right of a given line number. Then, by clicking the "debug" button to the right of the "run" button in the upper-right toolbar, you can have your app pause at the breakpoint, allowing you to inspect the state of your application.
-
The Logcat window can be difficult to parse, as the device tends to print out a lot of information that isn't necessarily relevant to your debugging process. However, Logcat provides a host of tools for pruning the errors that are displayed. You can limit console output by priority, or use the search tab to find the most relevant errors.
-
The Log class in Android Studio allows you to create custom sortable log statements. By importing
android.util.Log, you gain access to a host of logging commands intended to display the state of your application quickly. Combining these with Logcat's search tools can be a good way to ensure that your function calls are running properly. -
If you're curious about the implementation of core Android classes, you can use the tools provided by the IDE to view the inner workings of them. Android Studio will display an icon to the right of the line number to provide information on overriding methods for instance.