-
Jennifer Mankoff authoredJennifer Mankoff authored
access-trees.html 13.38 KiB
---
layout: presentation
title: Implementing Accessibility
description: More on how Accessibility is Implemented
class: middle, center, inverse
---
background-image: url(img/people.png)
.left-column50[
# Welcome to the Future of Access Technologies
Aria & Accessibility Trees: More on how Accessibility is Implemented
{{site.classnum}}, {{site.quarter}}
]
---
name: normal
layout: true
class:
---
# Important Reminder
## This is an important reminder
## Make sure zoom is running and recording!!!
## Make sure captioning is turned on
---
# Announcements
Reminder: what to do if you miss a class
Reminder: regrades
Summary: We'll keep doing it and add some moer details to it as requested
Visual calendar: We've heard this a few times. But I'm not sure where to put it or why canvas doesn't work. Can someone who's asking for this help us out with some user-centered desgin after class? :)
---
[//]: # (Outline Slide)
# Learning Goals for today
- Description of this week's assignment
- More on how accessibility is implemented
---
# First, Introducing your Website Report
We modified the assignment a bit
- It's now two weeks long
- It's optionally a group assignment (with others who reviewed the same website)
---
# Introduction
- What is the site or app for
- How did you assess it
- Overview table
| Task | Type (Web/Mobile/etc) | Testing Method | UARS found | Who Contributed |
|------|-----------------------|----------------|--------------|-----------------|
| ... | ... | ... | ... | |
|------|-----------------------|----------------|--------------|-----------------|
---
# Executive Summary
Summarize biggest problems (1-2 paragraphs)
| WCAG | Severe problems | Moderate problems | Minor problems |
|------|-----------------|-------------------|----------------|| ... | ... | ... | ... |
|------|-----------------|-------------------|----------------|
---
# Details
More detail on what needs to be done sorted by WCAG #
Include both problems and remedies
Easy to split this up among a group
---
# Make the report accessible
- Use headers
- Use proper color contrast
- Write alt text for photos
- Use meaningful hyperlinsk
- Turn in a word or google doc on Canvas
---
[//]: # (Outline Slide)
# Learning Goals for today
- Description of this week's assignment
- More on how accessibility is implemented
---
# What is a web page really?
| Content | Structure | Style | Behavior |
| :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: |
||
| Words and Images | HTML | CSS | JavaScript |
---
# What is a web page really?
| Content | Structure | Style | Behavior |
| :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: |
|||
| Words and Images | HTML | CSS | JavaScript |
---
# What is a web page really?
| Content | Structure | Style | Behavior |
| :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: |
||||
| Words and Images | HTML | CSS | JavaScript |
---
# What is a web page really?
| Content | Structure | Style | Behavior |
| :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: |
|||||
| Words and Images | HTML | CSS | JavaScript |
---
# Lifecycle of a browser* loading a page
.left-column40[
1. Fetch the page
2. Parse the page
3. Build up an internal representation of the web page
4. Display the page
]
.right-column60[
]
.footnote[*: As seen by Chrome]
---
# Parse and Display the Page
.left-column[

]
.right-column[
1. First line: <!DOCTYPE html>
- Ok: need to build an internal representation of the page
2. Line-by-line, go through the HTML
- If one of the tags links to a cascading style sheet (CSS) file, load and parse it
- If one of the tags links to Javascript (JS) for behavior, load and parse it
3. FINALLY display the page…
]
---
# Understanding content
- There are 100s of tags! See [Mozilla Developer Network](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element)!
- Some simple tags
- Title `<title></title>` (which nests inside your `<head></head>`)
- Headings `<h1></h1>` .. `<h6></h6>`
- Paragraphs `<p>`
- Ordered or unordered lists: `<ol></ol>`, `<ul></ul>`, with list elements `<li></li>`
- Horizontal rules `<hr />`
- Strong `<strong></strong>` which defaults to a bold style and emphasis `<em></em>` which defaults to italicized in most browsers.
---
# Adding content
- There are 100s of tags! See [Mozilla Developer Network](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element)!
- Some simple tags
- Some tags add semantic context
- `<header></header>`: The header or banner that displays the title of the page
- `<main></main>`: The bulk of the content of the page
- `<footer></footer>`: The footer is optional but you can put contact info and copyright date in there.
---
# Adding content
- There are 100s of tags! See [Mozilla Developer Network](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element)!
- Some simple tags
- Some tags add semantic context
- Some tags need additional information, added to a tag with attributes
- Links to other pages `<a href="filename"></a>`
- Links to images `<img src="img.jpg" alt="Description!"/>`
---
# Adding content
- There are 100s of tags! See [Mozilla Developer Network](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element)!
- Some simple tags
- Some tags add semantic context
- Some tags need additional information, added to a tag with attributes
- Some tags (comments) are important for documentation `<!-- -->`
---
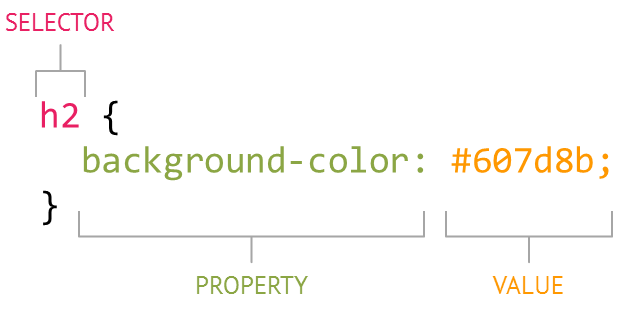
# Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
- Allows us to change the look and feel of the content on the page
- Style is separated into a .css file
- Makes styling multiple pages easier - Allows changing multiple pages easier
- Style sheets must be linked to an html page in the <head> for the styles to work
`<link href=“style.css” rel=“stylesheet” />`
- Great example is [CSS Zen Garden](http://www.csszengarden.com/)
<!-- --- -->
<!-- # CSS -->
<!-- .left-column50[ -->
<!-- - Files consist of one or more rule sets -->
<!-- - Each rule set has a selector which chooses which HTML elements you want to style -->
<!-- - Style properties are set with rules which are property/value pairs -->
<!-- - Syntax is important -->
<!-- - More on [CSS](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS) -->
<!-- ] -->
<!-- .right-column50[ -->
<!--  -->
<!-- From [W3Schools](https://code.makery.ch/library/html-css/part3/) -->
<!-- ] -->
---
# Layout in CSS
Layout can be [complicated](https://www.amazon.com/CSS-Awesome-Mug-Programmer-Developer/dp/B06Y13QC8N),
fortunately there is CSS [Flexbox](https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse154/flexboxducky/) or
[Grid](https://cssgridgarden.com/)!!

---
# Document Object Model (DOM) (1/3)
.left-column[

]
.right-column[
- This builds a hierarchy of document elements in what we call the **Document Object Model**
- The structure of this depends on our HTML (or the toolkit that generates your HTML)
- The structure of this influences layout
]
---
# Document Object Model (DOM) (2/3)
.left-column[

]
.right-column[
What does this hierarchy look like?
]
---
# Document Object Model (DOM) (3/3)
.left-column[

]
.right-column[
<div class="mermaid">%%{init: {'theme':'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#4CAF50', 'tertiaryColor': '#009688', 'fontSize': '16px', 'textMargin': '0px', 'text-align': 'left' }}%%
flowchart TD
A(Main Window)
B(Vertical Layout)
C("Spot the Heron" Label)
D(Picture of a heron in water with some reeds)
E(Horizontal Layout: Controls)
F(Left arrow)
G(Play)
H(Right arrow)
A --> B
B --> C
B --> D
B --> E
E --> F
E --> G
E --> H
classDef default fill:#009688,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px, color:white;
classDef reflect fill:#4CAF50,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px, color:white;
class A,B,C default
class A,B,C,D,E reflect
linkStyle default stroke: black,stroke-width:8px
</div>
]
---
# Let's compare that to an app
.left-column50[
**Interface Programmers** combine *library elements* (e.g. buttons and labels) according to *toolkit rules* &
constraints of *toolkit architecture* (common to all UI toolkits). Example: let's list all the components of this image:

]
.right-column50[
Discussion (post on Ed)
- What are the "components" in this image?
- What does the "interactor hierarchy" look like for this image
]
???
discuss with your neighbor
- what to draw; where to draw it
---
# How do we make it more interactive?
How about we add a button?
--
count: false
Wait? When you hear the word "button" in the context of a graphical user
interface (GUI), what do you think of?
--
count: false
How to tell a button where to place itself on the screen?
---
# Placment (layout)
What position do we use? What coordinate system do we use?
- An absolute position relative to the whole phone?
- A position relative to the whole app, but doesn't include the OS features (like status bars)?
- A position relative to the direct parent of the button, maybe a window *in* the app
--
Or should we let the toolkit decide what's best?
---
# Where should it go?
.left-column50[
Have to set up the layout first so we can see what we've added
This is a "Layout" problem - all UI toolkits have to support layout.
Layout is complicated because we want layout to handle things like resizing or changing from
portrait to landscape mode well.
]
--
.right-column50[
Specified using a <br>
component hierarchy (a tree)
<div class="mermaid">
graph TD
W(ConstraintLayout) --> V[Ab TextView--Hello World!]
W --> V1[fa:fa-square Button--Next ]
class W darkblue
class V1,V blue
</div>
Android's rendering of the same: 
]
---
# What should it do?
What do we tell the toolkit about the button?
--
We need to know when the user *interacts* with it
- This is called *Event Handling* Example:
```java
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// display a pop up with some text
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Hello!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
```
---
# Structure of a toolkit
Structure of a Toolkit
- Library of components
- Architecture
Note: these definitions have morphed over time, particularly as things have shifted to cross
platform development.
[Here's](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3057526/framework-vs-toolkit-vs-library/19790148#19790148)a reasonable set of definitions.
???
---
# Some Comparisons
| Android | Web |
| --- | --- |
| Java | HTML/CSS/JS |
| Layouts | CSS Flexbox or Grid |
| Interactor Hierarchy | Document Object Model (DOM) |
| Components | DIVS |
| Paint objects on a canvas | CSS |
| `onCreate` | `window.addEventListener("load", init);` |
| `View.OnClickListener#onClick` | `domElement.addEventListener("click", callback);` |
---
# Which of these Impacts Accessibility?
| Android | Web | Accessibility (eg s) |
|--------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
| Java | HTML/CSS/JS | Does the toolkit support access? |
| Layouts | CSS Flexbox or Grid | Comprehension/Magnification |
| Interactor Hierarchy | Document Object Model (DOM) | Navigation |
| Components | DIVS | Alternative text (toolkit dependent) |
| Paint objects on a canvas | CSS | Color choices |
| `onCreate` | `window.addEventListener("load", init);` | Proper Interaction with access API? |
| `View.OnClickListener#onClick` | `domElement.addEventListener("click", callback);` | See above |
---
# End of Deck